Bundle Splitting
stevepb (Public Domain)Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Introduction
- What is Webpack
- Developing
- Getting Started
- Development Server
- Composing Configuration
- Styling
- Loading Styles
- Separating CSS
- Eliminating Unused CSS
- Autoprefixing
- Loading Assets
- Loader Definitions
- Loading Images
- Loading Fonts
- Loading JavaScript
- Building
- Source Maps
- Code Splitting
- Bundle Splitting
- Tidying Up
- Optimizing
- Minifying
- Tree Shaking
- Environment Variables
- Adding Hashes to Filenames
- Separating a Runtime
- Build Analysis
- Performance
- Output
- Build Targets
- Multiple Pages
- Server-Side Rendering
- Module Federation
- Techniques
- Dynamic Loading
- Web Workers
- Internationalization
- Testing
- Deploying Applications
- Consuming Packages
- Extending
- Extending with Loaders
- Extending with Plugins
- Conclusion
- Appendices
- Comparison of Build Tools
- Hot Module Replacement
- CSS Modules
- Searching with React
- Troubleshooting
- Glossary
Although code splitting gives control over when code is loaded, it's not the only way webpack lets you shape the output.
Bundle splitting is a complementary technique that lets you define splitting behavior on the level of configuration. A common use case is extracting so called vendor bundle that contains third-party dependencies.
The split allows the client to download only the application bundle if there are changes only in the application code. The same goes for vendor-only changes.
To give you a quick example, instead of having main.js (100 kB), you could end up with main.js (10 kB) and vendor.js (90 kB). Now changes made to the application are cheap for the clients that have already used the application earlier.
Bundle splitting can be achieved using optimization.splitChunks.cacheGroups. When running in production mode, starting from webpack 4, the tool can perform a series of splits out of the box but in this chapter, we'll do something manually.
To invalidate the bundles correctly, you have to attach hashes to the generated bundles as discussed in the _Adding Hashes to Filenames_ chapter.
Adding something to split#
Given there's not much to split into the vendor bundle yet, you should add something there. Add React to the project first:
npm add react react-dom
Then make the project depend on it:
src/index.js
leanpub-start-insert
import "react";
import "react-dom";
leanpub-end-insert
...
Execute npm run build to get a baseline build. You should end up with something as below:
⬡ webpack: Build Finished
⬡ webpack: assets by path *.js 127 KiB
asset main.js 127 KiB [emitted] [minimized] (name: main) 2 related assets
asset 34.js 187 bytes [compared for emit] [minimized] 1 related asset
asset main.css 7.72 KiB [compared for emit] (name: main) 1 related asset
asset index.html 237 bytes [compared for emit]
Entrypoint main 135 KiB (323 KiB) = main.css 7.72 KiB main.js 127 KiB 2 auxiliary assets
...
webpack 5.5.0 compiled successfully in 5401 ms
As you can see, main.js is big. That is something to fix next.
Setting up a vendor bundle#
Before webpack 4, there used to be CommonsChunkPlugin for managing bundle splitting. The plugin has been replaced with automation and configuration.
To extract a vendor bundle from the node_modules directory, adjust the code as follows:
webpack.config.js
const productionConfig = merge([
...
{ optimization: { splitChunks: { chunks: "all" } } },
]);
If you try to generate a build now (npm run build), you should see something along this:
⬡ webpack: Build Finished
⬡ webpack: assets by status 128 KiB [emitted]
asset 935.js 124 KiB [emitted] [minimized] (id hint: vendors) 2 related assets
asset main.js 3.24 KiB [emitted] [minimized] (name: main) 1 related asset
asset index.html 267 bytes [emitted]
assets by status 7.9 KiB [compared for emit]
asset main.css 7.72 KiB [compared for emit] (name: main) 1 related asset
asset 34.js 187 bytes [compared for emit] [minimized] 1 related asset
Entrypoint main 135 KiB (326 KiB) = 935.js 124 KiB main.css 7.72 KiB main.js 3.24 KiB 3 auxiliary assets
...
webpack 5.5.0 compiled successfully in 4847 ms
Now the bundles look the same as in the image below.
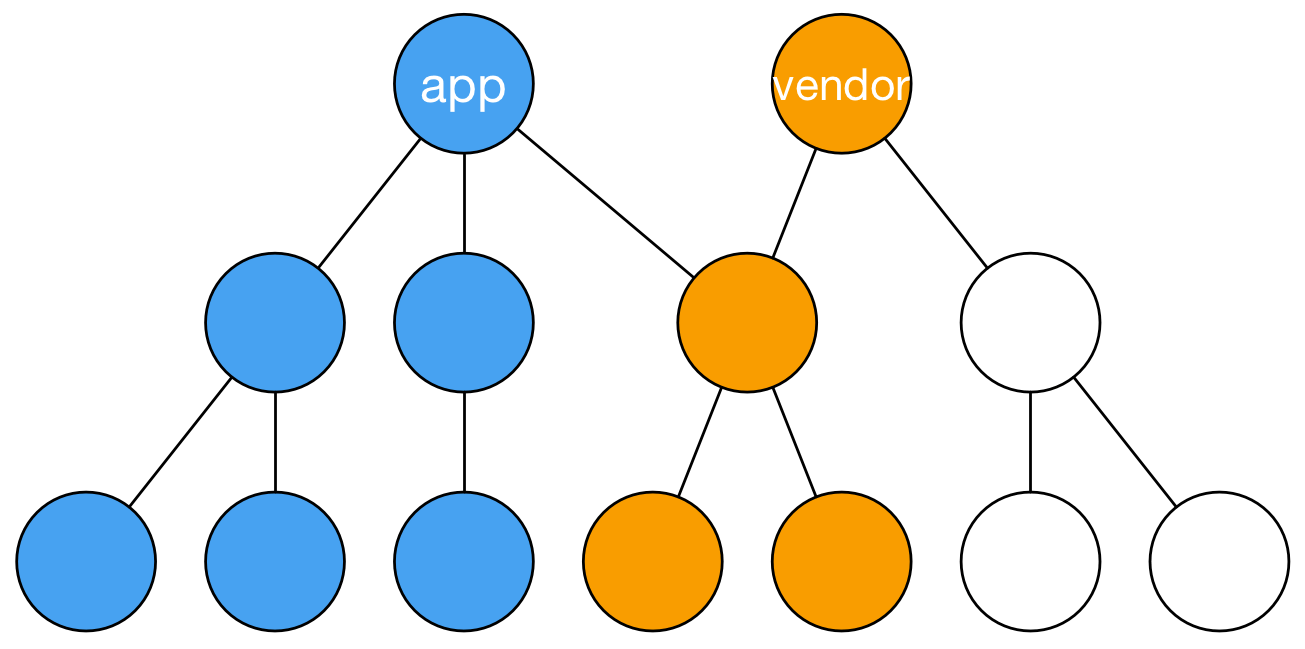
Controlling bundle splitting#
The configuration above can be rewritten with an explicit test against node_modules as below to gain more control:
webpack.config.js
const productionConfig = merge([
...
{
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
commons: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name: "vendor",
chunks: "initial",
},
},
},
},
},
]);
Starting from webpack 5, there's more control over chunking based on asset type:
const config = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
// css/mini-extra is injected by mini-css-extract-plugin
minSize: { javascript: 20000, "css/mini-extra": 10000 },
},
},
};
The `chunks: "initial"` option doesn't apply to code-split modules while `all` does.
Splitting and merging chunks#
Webpack provides more control over the generated chunks by two plugins:
AggressiveSplittingPluginallows you to emit more and smaller bundles. The behavior is handy with HTTP/2 due to the way the new standard works.AggressiveMergingPluginis doing the opposite.
Here's the basic idea of aggressive splitting:
const config = {
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.AggressiveSplittingPlugin({
minSize: 10000,
maxSize: 30000,
}),
],
};
There's a trade-off as you lose out in caching if you split to multiple small bundles. You also get request overhead in HTTP/1 environment.
The aggressive merging plugin works the opposite way and allows you to combine small bundles into bigger ones:
const config = {
plugins: [
new AggressiveMergingPlugin({
minSizeReduce: 2,
moveToParents: true,
}),
],
};
It's possible to get good caching behavior with these plugins if a webpack records are used. The idea is discussed in detail in the Adding Hashes to Filenames chapter.
webpack.optimize contains LimitChunkCountPlugin and MinChunkSizePlugin which give further control over chunk size.
Tobias Koppers discusses [aggressive merging in detail at the official blog of webpack](https://medium.com/webpack/webpack-http-2-7083ec3f3ce6).
Bundle splitting at entry configuration#
Starting from webpack 5, it's possible to define bundle splitting using entries:
const config = {
entry: {
app: {
import: path.join(__dirname, "src", "index.js"),
dependOn: "vendor",
},
vendor: ["react", "react-dom"],
},
};
If you have this configuration in place, you can drop optimization.splitChunks and the output should still be the same.
To use the approach with **webpack-plugin-serve**, you'll have to inject `webpack-plugin-serve/client` within `app.import` in this case.
Chunk types in webpack#
In the example above, you used different types of webpack chunks. Webpack treats chunks in three types:
- Entry chunks contain webpack runtime and modules it then loads.
- Normal chunks don't contain webpack runtime. Instead, these can be loaded dynamically while the application is running. A suitable wrapper (JSONP for example) is generated for these. You generate a normal chunk in the next chapter as you set up code splitting.
- Initial chunks are normal chunks that count towards initial loading time of the application. As a user, you don't have to care about these. It's the split between entry chunks and normal chunks that is important.
Conclusion#
The situation is better now compared to the earlier. Note how small main bundle compared to the vendor bundle. To benefit from this split, you set up caching in the next part of this book in the Adding Hashes to Filenames chapter.
To recap:
- Webpack allows you to split bundles from configuration entries through the
optimization.splitChunks.cacheGroupsfield. It performs bundle splitting by default in production mode as well. - A vendor bundle contains the third-party code of your project. The vendor dependencies can be detected by inspecting where the modules are imported.
- Webpack offers more control over chunking through specific plugins, such as
AggressiveSplittingPluginandAggressiveMergingPlugin. Mainly the splitting plugin can be handy in HTTP/2 oriented setups. - Internally webpack relies on three chunk types: entry, normal, and initial chunks.
You'll learn to tidy up the build in the next chapter.
This book is available through Leanpub (digital), Amazon (paperback), and Kindle (digital). By purchasing the book you support the development of further content. A part of profit (~30%) goes to Tobias Koppers, the author of webpack.